Gothic Style: What Ideas Transformed Architecture?
Table Of Content
It was designed in the Gothic Revival architectural style by William Douglas Lee, and it was completed in 1926. It has been listed on the National Register of Historic Places since March 8, 2010. For as distinctive and inspiring as the era was, our blog enlists all that there is to know about Gothic Architecture, its origin, key features, prominent Gothic buildings and their architects. So, without any further ado, let us deck ourselves with the beauty of Gothic architecture and its journey. Translating to the “Silk Exchange”, Llotja de la Seda was a commercial building where merchants and traders met to exchange goods. It is one of the greatest examples of Gothic Architecture in the region of Valencia, which shows the immense wealth that trade brought to the city.
What is Gothic Architecture?
The cathedral was the center of urban life, acting as a market, meeting hall, and artistic showcase. Extensive decorative programs told biblical stories for largely illiterate congregations. Politically, Gothic architecture reflected the growing authority of the Church and monarchies. Architecturally, the move from heavy Romanesque buildings to soaring Gothic structures mirrored the shift from feudalism to stronger centralized authority.
Reims Cathedral – Reims, Grand Est, France
Built over the course of just 50 years—a relatively short time in Gothic architecture—the Amiens Cathedral is a wonderful example of the High Gothic. It represents the apex of trying to reach for the heavens and stands as France's largest cathedral. The French Flamboyant style, developing from the Rayonnant style, emphasized even greater decorative effects by employing more curved shapes. The name comes from the French word “flambé” meaning flame, as the curving ornate lines of edifices were thought to resemble flames. It’s thought by some scholars that the intricate patterns and motifs from illuminated manuscripts were a noted influence.
What are the iconic examples of Gothic architecture around the world?
The High Gothic years, from 1250 to 1300, were still dominated by France, but Britain, Germany, and Spain produced variations of the style, such as Cologne Cathedral, London's Westminster Abbey, and Milan's Duomo. Italian Gothic architecture stood apart for its brick and marble construction rather than stone. This Cathedral took 600 years to complete, with construction beginning in 1248 was abandoned in 1473, and remained unfinished for 350 years, to be resumed in the 1840s and was completed in 1880. The Cologne Cathedral was the largest in Northern Europe and had the second-tallest spires built in a Germanic Gothic style. The cathedral has witnessed several tank battles and bomb hits, and it has been ongoing repair since after the war to date.
Exploring the Art and Science of Glazes in Ceramics
Stained glass is an integral part of nearly all Gothic Architecture, particularly in religious buildings. Stained glass was an essential part of the catholic church’s plan to teach the stories of the bible to a largely illiterate European population. The stained glass windows at Chartres Cathedral in France are some of the most impressive in all of Europe. The blue pieces of glass were renowned in the middle ages for being extremely expensive to produce.
Where to Find Gothic Architecture
This has resulted in a rather unusual unity of style, as many other Gothic buildings were built over the span of hundreds of years and therefore were subject to several different phases and styles during their construction. The Medieval Cathedral of Seville was built on the site of a mosque known as Almohad Mosque. The builders of the cathedral used some elements of the mosque such as some columns to help build certain parts such as the Giralda, the bell tower that was converted from a minaret. After the Reconquista in 1248, the cathedral was built to display the wealth of the city. The cathedra’s interior boasts a nave that is unmatched in length by any other cathedral in Spain. In England, the stained glass windows also grew in size and importance; major examples were the Becket Windows at Canterbury Cathedral (1200–1230) and the windows of Lincoln Cathedral (1200–1220).
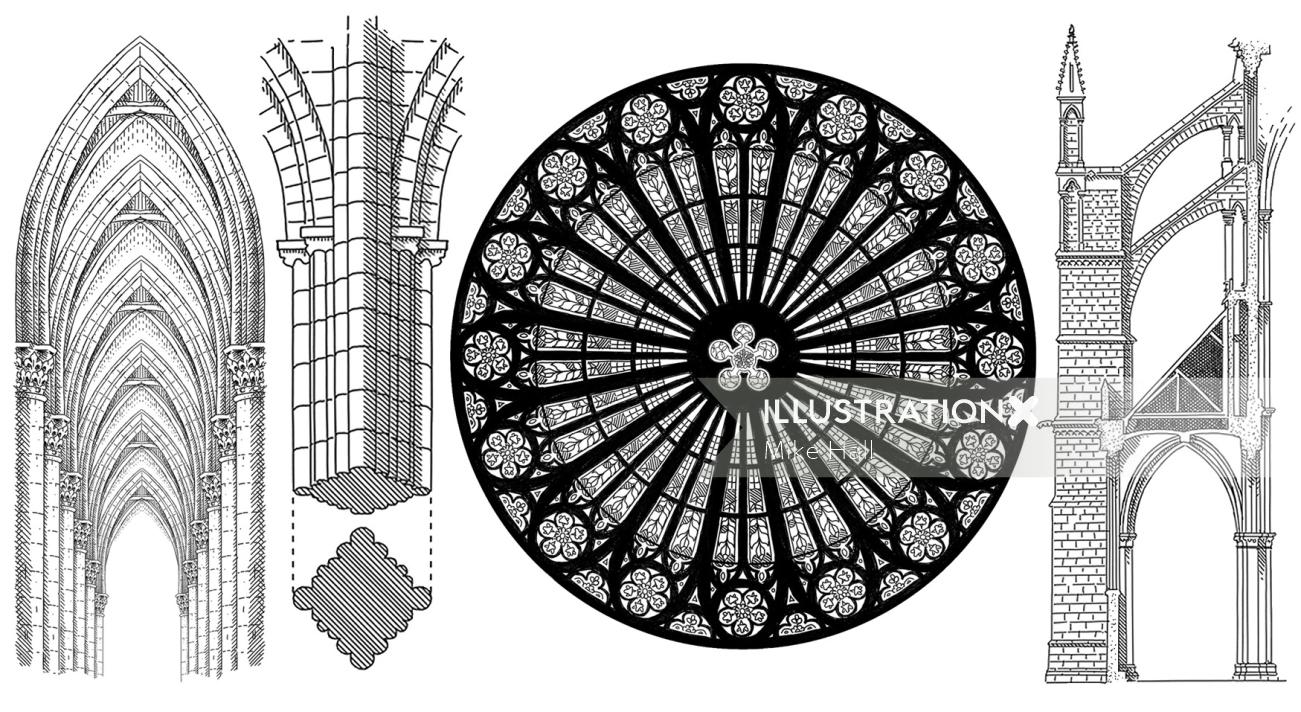
In order to build extremely tall structures with tall windows, Gothic architects began to use ribbed vaults—or arched vaults placed parallel to each other to support a rounded roof—rather than traditional vaulted beams. Not only did these intersecting vaults create visual interest, but also they offered more support to tall Gothic structures. Scary-looking gargoyles are a common finishing touch on the roofline of Gothic structures.
The interior has innovative four-part rib vaults that allow for a more uniform appearance while increasing the height. During the reigns of Louis XIV and his successor Louis XV, the cathedral went through more extensive alterations. During the chaotic and destructive French revolution, the cathedral was badly damaged with much of the religious iconography destroyed. The famous Gothic church also experienced damage during World War II when several of the stained glass windows were destroyed by bullets which were later remade, but in a more modern design that incorporated geometric designs. Early Gothic churches used rib vaults that were divided into six parts resulting in the columns in the nave alternating in size to support the vaults.
Amiens Cathedral
Renovations and reconstruction have continued throughout the history of the church, which is one of Paris' most visited sites. Officials have promised that the building will be fully restored in time for the 2024 Paris Olympics. In order to incorporate higher ceilings and taller windows into their designs, Gothic architects utilized a new method of structural support called rib vaulting. Rib vaulting involves the use of intersecting barrel vaults—arches placed parallel to one another in order to support a rounded roof. These elements enabled Gothic masons to build much larger and taller buildings than their Romanesque predecessors and to give their structures more complicated ground plans.
The skillful use of flying buttresses made it possible to build extremely tall, thin-walled buildings whose interior structural system of columnar piers and ribs reinforced an impression of soaring verticality. As was characteristic in the Gothic era, the Rayonnant style took on regional variations. Romanesque churches from the 10th to the 12th centuries are noted for their use of barrel vaults, rounded arches, towers, and their thick walls, pillars and piers. Housing the relics of saints, the churches were part of the pilgrimage routes that extended throughout Europe, as the faithful visited the holy sites to seek forgiveness for their sins and attain the promise of Heaven. Another noticeable feature of Gothic architecture is the use of spires and towers in their design.
The new flèche, of wood covered with lead, was decorated with statues of the Apostles; the figure of St Thomas resembled Viollet-le-Duc.[82] The flèche was destroyed in the 2019 fire, but is being restored in the same design. Gothic cathedrals often lead you to kaleidoscopic landscapes through their stained glass windows. Adorned on the Gothic building envelope as a lancet or rose design, these windows let in flamboyance like none other. Crafted from the tales of Biblical novellas, these windows add a decorative character to the elevation as well as the interiors. The churches were of Basilica type with a central Nave and side aisles separated by arcades.
10 Best Gothic Romance Movies, Ranked - Collider
10 Best Gothic Romance Movies, Ranked.
Posted: Sun, 14 Apr 2024 07:00:00 GMT [source]
The most important developments in later Gothic architecture were the Rayonnant Style followed by the Flamboyant Style. In painting, the most significant singular style was that of the Italian Sienese School, and the illuminated manuscript painting of the International Gothic Style. The architecture that informed the Gothic period drew upon a number of influences, including Romanesque, Byzantine, and Middle Eastern.
The tallest church tower in the world is at Ulm Minster, a Gothic Church in Germany, and the tallest nave on Earth is at Beauvais Cathedral in France. The striking heights that Gothic Builders were able to achieve were thanks in large part to new innovations, like the Flying Buttress. The towering heights were meant to inspire the populations of Europe, making them awestruck at the power of the Christian Church.
In addition to religious figures, many Gothic cathedrals are heavily ornamented with strange, leering creatures. Originally, the sculptures were waterspouts to remove rain from the roofs and extended away from the walls, protecting the foundation. Since most people in Medieval days could not read, the carvings also took on the important role of illustrating lessons from the scriptures. Earlier Romanesque churches relied on barrel vaulting, where the ceiling between the barrel arches actually looked like the inside of a barrel or a covered bridge.
The windows are usually very tall and arched, or round, and were intended to let in as much natural light as possible. You'll often find tracery, a decorative, stone support, as well as biblical scenes in Gothic stained glass windows. The innovative structural elements that would support these mega-cathedrals would define Gothic architecture's aesthetics. First, the lightness of these structures came from the use of pointed arches, borrowed from Islamic architecture that was built in Spain around the same time. The arch reduced stress on other structural elements, therefore allowing the columns that support the arch to become more slender and taller- so much so that the columns extended all the way to the roof, forming part of the vault.
Let's rewind the conversation and backtrack to the era of revolts, revolutions, the birth of unconventional movements, princesses, and knights, or as we date it, the mediaeval era. Amidst all the fire and uncanny sights, there was the emergence of a period that worshipped the grotesque. Initially referred to as the Opus Francigenum or French work, the urban fabric was about to be hit by a dominant European influence from the aesthetic of Roman Catholic churches.
Comments
Post a Comment